Everyone around the world has been introduced to the term “blockchain” one way or another. This technology has revolutionized the digital world. All of us are aware of its significance in the financial sector, but this technology is opening up new ventures in almost every domain. Companies or even individuals want to have more transparency in their businesses, and Blockchain provides a well secure and safe system.
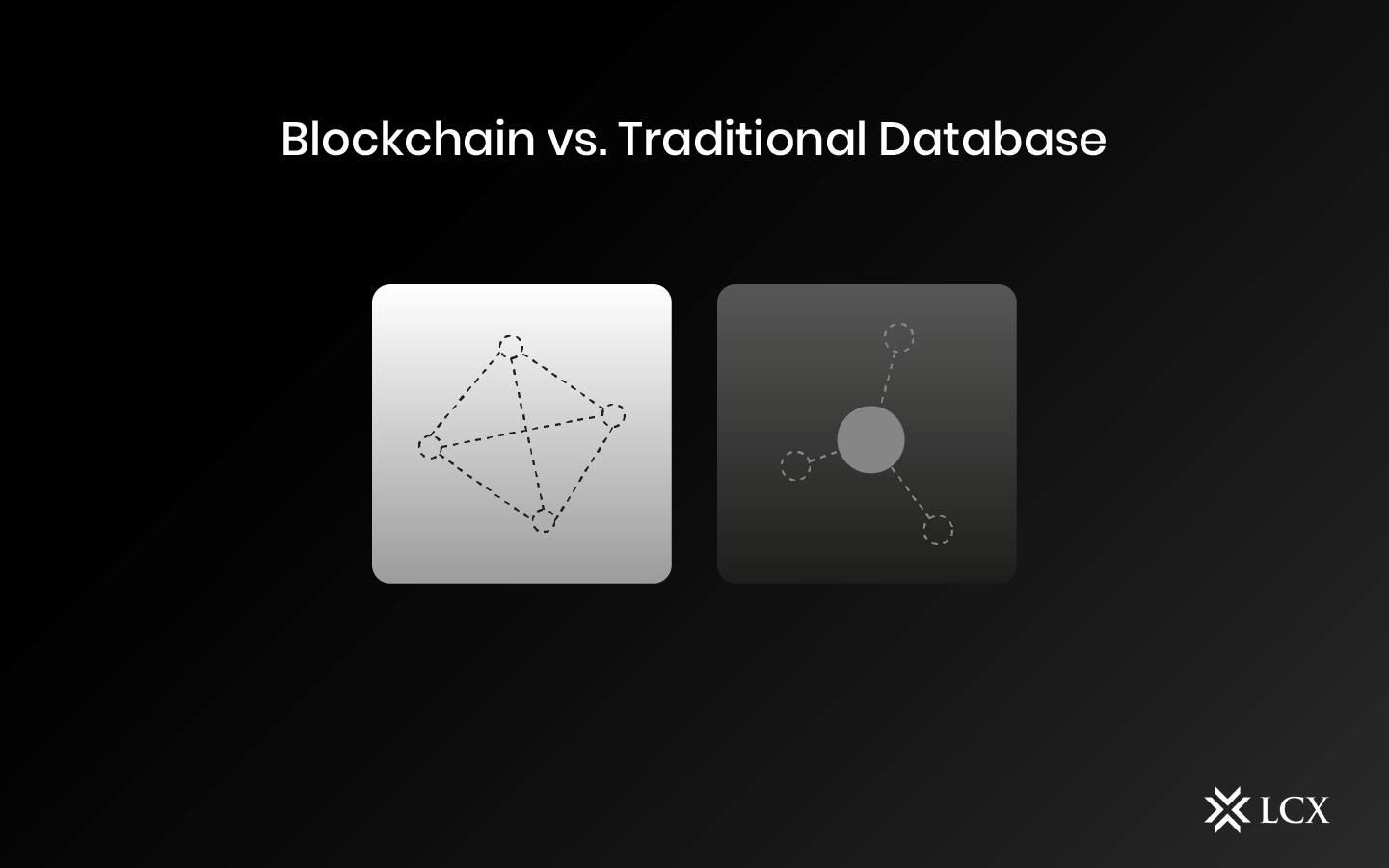
Blockchain is considered a database, and while it is similar to traditional databases in some ways, the two are fundamentally different.
Blockchain
Several decentralized nodes make up blockchain databases. Every node helps with administration as each of them have access to uploading the new data to the database and for checking the latest updates on Blockchain. A majority of nodes must obtain consensus before addition to the Blockchain may be performed. This consensus technique keeps in check the network’s security and not let it be vulnerable to malicious activities such as hacking.
Traditional Database
Client-server network architecture is used in traditional databases. A user (known as a client) can change data that is kept on a central server. The database is controlled by a certain authority, which verifies a client’s credentials before giving access. Because this authority is in charge of database administration, data can be compromised if the authority’s security is deleted or altered.
Difference between Blockchain and Traditional database
| Blockchain | Traditional Database |
| Blockchain does not have a centralized control system. It enables several parties to share data without requiring a central system or administrator. As a result, the data is kept safe and secure. | The administrator has authority over it from a central location. Any change in the data can cause the information to change all over the place. Anyone with access to the centralized database can corrupt or destroy the data. It has resulted in hacking and forgery cases. |
| Blockchain technology faces scalability issues because of its dependency on all the decentralized nodes. | Because permissions are centralized and the powers to alter data are in the hands of a few, traditional databases can handle enormous volumes of transactions per second. The client-server design lowers reliance on nodes, which are replaced with isolated server centers. |
| Blockchain has the potential to boost data transparency and trust, resulting in increased creativity, productivity, and quality. | Traditional databases fail to provide the level of transparency offered by BlockchainBlockchain. |
| Cryptography is required to hide information on Blockchain. There is no information confidentiality. Everyone in the system is aware of it. | When it comes to traditional databases, information is only accessible to members. |
| As Blockchain is a public distributed ledger, it can not be customized by an individual’s choice. | A traditional database offers numerous customization choices. Permissions, Privileges, and set-up requirements can all be optimized because traditional databases are managed centrally. Developers can update the front end and add plugins to the database to make it customer-centric. |
| The user can contribute more data in the form of additional blocks in the Blockchain. The old data will not be destroyed; it will stay in the system and be accessible to the public. | The client performs four roles in a typical database: Create, Read, Update, and Delete. These are the four steps in the CRUD process. |
| The information that is current and the information that was previously available coexist. It generates a database with its histories in it. This property of Blockchain makes it handy for tracing records and determining a product’s validity. | The information in a centralized or traditional database is current at any given time. |
Use Blockchain for:
- Real-time data exchange
- Financial transfer
- Identifying and authenticating records
- dApps (Decentralized applications)
Use traditional database for:
- Relational Data
- Confidential records
- Conventional storage systems
- Data that would be frequently modified
Conclusion:
It is not difficult to choose your next data storage technique. While databases are faster and more accurate, Blockchain provides innovation, verification, and automation. Because of its verification approach, Blockchain has a performance constraint. This obviously indicates that you should avoid Blockchain if the speed of execution is critical. When a crucial business process needs to be supported or scaled simultaneously, traditional databases are an excellent solution. When it comes to the Blockchain, the read and write process is also not straightforward, which makes the database more appealing for general-purpose applications. Finally, if you want trust, transparency, and verification, Blockchain is the way. On the other hand, traditional databases are suitable for high-performance services or apps.