Blockchain is a decentralized, immutable ledger that makes recording transactions and administering assets (both tangible and intangible) in a corporate network much easier. On a blockchain network, virtually anything of value can be recorded and exchanged, reducing risk and costs for all parties. The peer-to-peer architecture of blockchain enables data to be stored globally on millions of servers. It is also described as a peer-to-peer, decentralized, distributed ledger technology that operates without needing a third-party intermediary or centralized authority, in contrast to traditional institutions that rely on intermediaries. Due to its increased security, transparency, and immutability, blockchain is currently the most discussed technology. Blockchain technology is attracting developers and specialists with its potential to revolutionize how industries and businesses operate.
Understanding Public Blockchains
Public blockchains are decentralized networks in which anyone can participate, validate transactions, and preserve the integrity of the blockchain. These networks are accessible to the general public, which allows anyone to join, view, or write transactions. Private blockchains, on the other hand, limit access to a select group of participants, reducing decentralization while augmenting privacy and control.
The combination of economic incentives with cryptographic verification using procedures such as proof-of-work (Bitcoin) or proof-of-stake (Ethereum) secures public blockchains (Ethereum) through cryptoeconomics. These blockchains are regarded as “completely decentralized” in general. Public blockchains provide a method for protecting app users from their developers by demonstrating that specific actions are beyond the authority of even the app’s developers. Because public blockchains are accessible, many organizations are likely to employ them without the need for third-party verification.
The anonymity of the public blockchain is an additional factor in its popularity. It is a secure, open platform where users can conduct business effectively and safely. In addition, users are not required to reveal their real names or identities in order to participate. Hence, the network activity cannot be traced if the identity is protected.
Fundamentals of Public Blockchains
- Decentralization and Consensus Mechanisms
At the heart of public blockchains lies decentralization, which ensures that no single entity has control over the network. Through a consensus mechanism such as Proof of Work (PoW) or Proof of Stake (PoS), participants collectively validate transactions and maintain the integrity of the blockchain. This distributed consensus ensures transparency, security, and immutability of the recorded data, making it tamper-proof and resistant to malicious attacks.
- Transparency and Auditability
Public blockchains offer unprecedented transparency by providing a public ledger visible to all participants. Every transaction, from financial transfers to smart contract execution, is recorded on the blockchain, ensuring an immutable record of all activities. This transparency fosters trust among participants, eliminates the need for intermediaries, and enables efficient auditing processes.
- Cryptographic Security
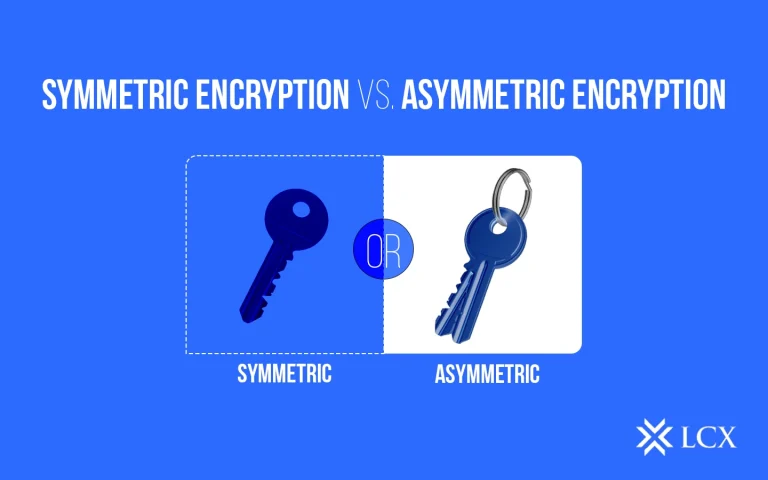
Public blockchains employ advanced cryptographic techniques to secure transactions and protect data integrity. Transactions are verified through cryptographic signatures, ensuring that only authorized parties can engage in the blockchain network. Additionally, encryption techniques safeguard sensitive data, mitigating the risks of unauthorized access and data breaches.
Implications for Businesses and Industries
- Supply Chain Management
Public blockchains have the potential to revolutionize supply chain management by providing end-to-end visibility, traceability, and accountability. With a transparent and immutable record of every transaction and movement of goods, businesses can ensure authenticity, prevent counterfeiting, and streamline logistics. This increased transparency also empowers consumers to make informed choices, fostering trust in the products and brands they engage with.
- Financial Services
The financial industry stands to benefit significantly from public blockchains. With decentralized ledgers, transactions can be executed faster, cheaper, and with enhanced security. Smart contracts, or programmable self-executing agreements, automate processes such as loan approvals, settlements, and regulatory compliance, reducing costs and eliminating intermediaries. Public blockchains also open up new avenues for financial inclusion, enabling individuals without access to traditional banking systems to participate in the global economy.
- Healthcare and Identity Management
Public blockchains offer a secure and decentralized solution for managing personal data and identities. By leveraging blockchain technology, patients can control and share their medical records securely with healthcare providers, enhancing interoperability and improving patient outcomes. Furthermore, public blockchains can address identity verification challenges, reducing fraud and enabling individuals to have control over their digital identities.
Conclusion
Public blockchains are at the forefront of a technological revolution, offering an innovative and inclusive infrastructure that challenges traditional systems. By leveraging the power of decentralization, transparency, and cryptographic security, public blockchains have the potential to reshape industries, foster trust, and empower individuals worldwide. Businesses and governments must embrace this transformative technology, while also addressing regulatory and societal considerations, to unlock the full potential of public blockchains and build a more equitable and transparent future.