The crypto community continues to expand with the introduction of new projects regularly. New businesses are springing up to offer their products and services in the growing blockchain ecosystem. The SAFT agreement helps crypto-related companies finance their operations. As a result, it is frequently referred to as an alternative to an Initial Coin Offering (ICO) .
What Is The SAFT Agreement?
SAFT stands for Simple Agreement for Future Tokens. It is an investment agreement between accredited investors and crypto developers. Under this agreement, the investors agree to finance the developers’ project in exchange for discounted tokens at a future date.
Based on specific parameters, accredited investors are legally permitted to invest in certain restricted and severely regulated securities.
It is a legal agreement. Thus it permits the projects to be funded without causing any federal or state breaches. Securities laws in the United States govern this contract. However, the tokens transferred under this arrangement are not classified as securities in the United States and cannot be compared to SAFT.
How Does It Work?
SAFT agreements compensate the authorized investors for early financing. The cryptocurrency company will issue tokens at a discount rate. The discount price is the value of a single token multiplied by the discount rate during a triggering event.
A SAFT essentially allows the company to extend the valuation of the token. Certain SAFT agreements may also have a valuation cap. Thus, when parties raise capital through a SAFT with a valuation cap, they essentially negotiate that valuation. SAFT does not need to be considered a debt on the balance sheet. However, If the company fails before the conversion of cash into tokens, it will pay the investor an equivalent amount to their capital investment before paying to its shareholders.
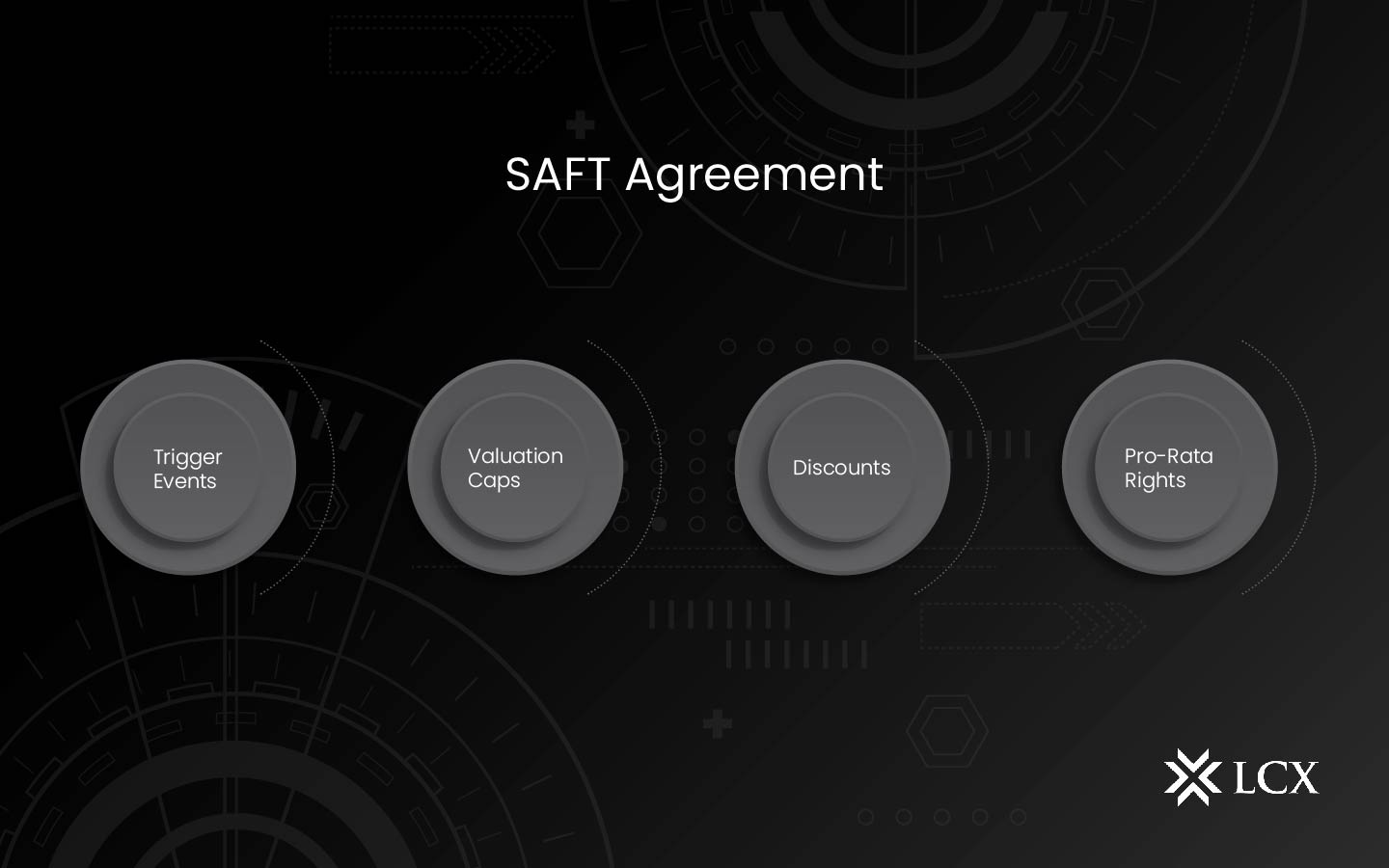
SAFT Consists Of:
A few main terms need to be negotiated between both parties before signing a SAFT.
- Trigger Events: When you trigger an event such as a merger or an ICO, the future tokens are converted into tokens. The SAFT is useless if the company goes bankrupt or the triggering events never happen. A future token investment could be the catalyst. The quantity of tokens received by SAFT investors is the same as that received by prospective investors.
- Valuation Caps: A seed-stage investor takes a considerable risk in the early phases. A valuation cap overcomes this problem for the investor. The investor’s ownership percentage is determined by a valuation cap, which sets a maximum token value. Because there is no cap on the token’s worth, the percentage available to SAFT investors decreases as the company’s value rises.
- Discounts. A discount rate gives the SAFT investor a deal on the tokens’ value at the moment of the triggering event. It is a reduction in the predicted future price.
- Pro-Rata rights: The SAFT investor has pro-rata rights, which allow them to participate in future fundraising rounds. While this is advantageous to the authorized investor, prospective investors may object if they want the round to themselves.
How Is It Different From SAFE?
SAFT and SAFE are two separate agreements.
A Simple Agreement for Future Equity (SAFE) allows investors who put cash into a startup to convert that stake into equity later. In contrast, developers use funds from the sale of SAFT to develop the technology required to create a functional token and then provide these tokens to investors expecting to sell them at some future market.
How is it Different from ICO?
SAFTs are frequently mistaken for Initial Coin Offerings (ICOs). A startup sells its tokens to regular, pre-approved users in an initial coin offering (ICO) on a launchpad. SAFTs, on the other hand, only work with accredited investors.
Benefits OF SAFT
- Standardization may be possible. SAFT contracts might lead to industry uniformity, which regulators would welcome. It would also allow startups to continue to fund the development of their goods through digital token sales.
- Enhanced security. Because SAFT contracts are securities, they must go through a verification procedure, and ICO scams would be considerably reduced. In addition, the SEC would monitor the transactions at every stage of the process.
- A larger pool of potential investors. The benefits of SAFT agreements alone could broaden the token sale investor base. They would give some protection to investors, but they would also provide the public with the openness they desire.
Challenges
- Only approved investors have access to the SAFT framework. Thus, the general public and individual investors are not permitted to participate.
- It may appear that SAFT contracts are working against the crypto movement. The whole point of cryptocurrency and digital currencies is to achieve independence and freedom. Some people may object to them being a standardized component.
- Reach is limited. The federal laws of the United States were used to create SAFTs. As a result of their lack of international application, they may not garner as much global engagement.
LCX has developed a fully digital and automated alternative to SAFT which is managed by a token sale manager. When an investor participates in a token sale on LCX, they do not require SAFT in order to guarantee their token returns, ensuring the completion of their investment. The investors on LCX can instantly access the tokens after investment. However, the tokens can be locked depending on the vesting terms agreed upon while buying the tokens. This new and innovative technology is revolutionizing the investing process and making investments in new projects safe and more reliable.
Conclusion
SAFT is the new investment vehicle compliant with the U.S security regulations. Although the agreement is quite simple and effective, it needs careful negotiation and understanding. Thus, it is better to consider it in the presence of an attorney. This way, it will be a meaningful transaction for both parties. It is a high-risk investment in the token economy and is only accessible to accredited investors. Also, it is a pretty recent development. Thus we need to see how regulators will respond to this agreement in the future.